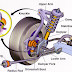
Suspension is the system of tires, tire air, springs, shock absorbers and linkages that connects a vehicle to its wheels and allows relative motion between the two.
Suspension systems serve a dual purpose — contributing to the vehicle's roadholding/handling and braking for good active safety and driving pleasure, and keeping vehicle occupants comfortable and a ride quality reasonably well isolated from road noise, bumps, and vibrations
Suspension systems serve a dual purpose — contributing to the vehicle's roadholding/handling and braking for good active safety and driving pleasure, and keeping vehicle occupants comfortable and a ride quality reasonably well isolated from road noise, bumps, and vibrations
.
The components of the suspension consist of:
- Tires
- Wheels
- Shock absorbers
- Mcpherson struts
- Springs
- Sway bars
- Torsion bars
- A arms
- Lower control arms
- Axles
- Alignment
- Tire pressure
The various components of the suspension systems of every vehicle are
designed to counteraffect the forces of gravity and inertia! Even though
every car is different, every system accomplishes the same objective:-
- Keeping tires on the road surface. Engineers call this "road holding". It's important for the tires to stay in contact at all times, because friction between the tires and the ground is what lets the car accelerate, stop and corner. The suspension keeps the weight centered to maintain the grip.
- Stable steering and handling. The suspension keeps the car or truck body from tipping or rolling in a corner.
- Passenger comfort. Keeps the cabin isolated from the bumps on the road. Suspensions absorb that up-and-down energy and disperse it without too many bobbles.
How does the Suspension System work?
The suspension system connects
your vehicle to its wheels. It is designed to counteract the forces of
gravity, propulsion and inertia that are applied to your vehicle as you
accelerate, slow down or stop in such a way that all four wheels remain
on the ground!
The tires - which are mounted on your vehicle’s wheels (or rims) - are the most important and visible components of the system. They transfer the power of the engine to the ground when your vehicle moves and they counter that motion when it stops.
As you drive over a bumpy road, shocks are absorbed by the combined work of a shock absorber (or damper) and a coil or leaf spring mounted on each wheel. The spring is a device that stores energy in order to supply it later on. It is actually the spring that handles the abuse of the road by allowing the wheel to move up and down with respect to the frame of the vehicle. In return, the shock absorber softens the suspension moves entailed by the spring by “absorbing the shocks”. The shock absorber is a steel or aluminum hydraulic cylinder filled with oil and pressurized with nitrogen. As the suspension moves, a piston is forced to move through the oil-filled cylinder. The energy produced from the motion of the piston is dissipated as heat which in turn is absorbed by the oil.
Types of suspension system for independent system
- MacPherson strut type
- Double wishbone type
- Semi trailing arm type
MacPherson strut type :
This system is usually use for most widely in independent suspension
system for small and medium sized cars.These type are so popular so in
FF(Front engine and front wheel transmission)type of car,used as the
rear suspension.
Characteristic for MacPherson: The construction of the suspension is relatively simple. MacPherson type,have small number of parts,so when it component is less,then less weight.The effects is unsprung can be reduce.
The space for the suspension is small,the usable space in the engine compartment can be increased. Since the distance between suspension support point is great,there is a little disturbance of the front wheel allingment due to installation error or part manufacturing error.Therefore, except for toe-in,allingment adjustment ordinarily unnecessary.
Double wishbone type:
Characteristic for MacPherson: The construction of the suspension is relatively simple. MacPherson type,have small number of parts,so when it component is less,then less weight.The effects is unsprung can be reduce.
The space for the suspension is small,the usable space in the engine compartment can be increased. Since the distance between suspension support point is great,there is a little disturbance of the front wheel allingment due to installation error or part manufacturing error.Therefore, except for toe-in,allingment adjustment ordinarily unnecessary.
Double wishbone type:
This is usually used for front suspension for small trucks and for front
and rear suspension for passenger cars. Characteristic for double
wishbone: Wheels are mounted to the body via upper and lower arm.
Suspension geometry can be designed as desired according to the length
of the upper and lower arm and their mounting angles.
For example if upper and lower arm are parallel and have equal length,the tread and the tire-toe ground camber of the tire will change.As a result,it is not possible to obtain adequate conering performance.In addition, in the tread will cause excessive tire wear.
To solve this a design is normally employed in which the upper arm is made shorter than the lower arm so that the tread and the tire-to-ground camber of the tire fluctuate less.
Semi trailing arm type
For example if upper and lower arm are parallel and have equal length,the tread and the tire-toe ground camber of the tire will change.As a result,it is not possible to obtain adequate conering performance.In addition, in the tread will cause excessive tire wear.
To solve this a design is normally employed in which the upper arm is made shorter than the lower arm so that the tread and the tire-to-ground camber of the tire fluctuate less.
Semi trailing arm type
Is used for the rear suspension in a few models.With this suspension,the amount by which the toe angle and camber change(due to the up-and-down motion of the wheels) can be controlled at the design stage, in order to determined the handling characteristics of the vehicle.
Signs of troubles related to the Suspension System:
- Excessive tire wear
- Poor steering control or off-center steering wheel
- Excessive bouncing over road bumps
- Loss of control during sudden stops
- Excessive swerving while changing lanes
- Front-end nose diving during quick stops
- Vehicle sag in front or rear
- the source : mechanics tips